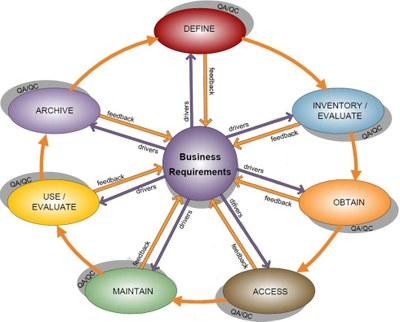
Data and information are organizational assets. Metadata enables data developers and consumers in locating, assessing, and utlizing these assets through out the data lifecycle:
Define – document data requirements, standards, and workflows
Inventory/Evaluate – locate available data and determine fitness for use
Obtain – determine options and best method to access available data
Access –publish info about data and make it available to the user community
Maintain –assess data currency, relevance, and need for updates
Use/Evaluate – monitor fitness of the data to meet current mission/project needs
Archive – document the data schema for future use and determine components and formats to preserve
From a management perspective, metadata supports the following objectives.
Data Management
- preserve the data history so that it can be re-used or adapted,
- assess the age and character of data holdings to determine which data should be maintained, updated, or deleted,
- instill data accountability by documenting what you do and don't know about your data
- limit data liability by explicitly designating the effective and administrative limits of use of the data.
Project Management
- plan and document the data types and content needed to support the project
- monitor data development by regular review of the process steps completed and recorded within the metadata
- provide all project participants a common language of attributes and process methods and a place to record and share their progress
- access the lineage and content of outsourced data production by requiring robust metadata as a contract deliverable.
Preservation of Institutional Knowledge
As personnel leave an organization so does the institutional knowledge. If the data purpose and content are not documented, the data lose value and new personnel may chose recreate it or some variation. In addition, without metadata, data producers are unable to locate and apply data resources created by others. Though metadata management does require staff time and other resources, the expense is offset by savings associated with the ability to locate, assess, and build upon existing data.
View the The Value of Metadata (pdf, ppt) for more information.